Laboratory
 Contact and Home blood draw: 0331-8822-712
We provide state-of-the-art robotic systems for rapid and accurate testing of a wide-range of parameters in blood and other biological fluids. We have reported results for routine tests in a record 30 min time as well, however, we try our utmost to limit our needle to report time to 1-hour. For all general tests such as CBC, blood chemistry including liver and renal function tests as well as inflammatory markers such as CRP, we aim to provide your patients accurate and rapid results within the 1-hour time frame.
Contact and Home blood draw: 0331-8822-712
We provide state-of-the-art robotic systems for rapid and accurate testing of a wide-range of parameters in blood and other biological fluids. We have reported results for routine tests in a record 30 min time as well, however, we try our utmost to limit our needle to report time to 1-hour. For all general tests such as CBC, blood chemistry including liver and renal function tests as well as inflammatory markers such as CRP, we aim to provide your patients accurate and rapid results within the 1-hour time frame. 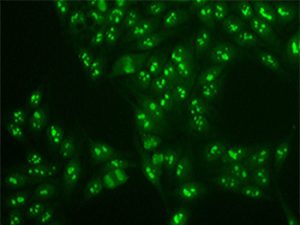
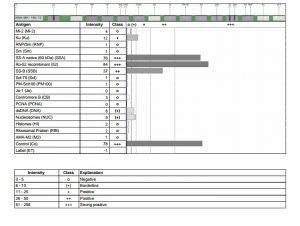
Immunofluorescent staining for ANA (Nucleolar pattern) (Photo copyright ImmunoCure Laboratory)
Anti-Nuclear Autoantibodies (ANA) are critical in a multitude of autoimmune diseases. ANA testing is performed on several major methods: Immunofluorescence (IIFT), Immunoblot (IB), and ELISA. However, IIFT is the GOLD standard for the diagnosis of auto-antibodies especially ANA. At ImmunoCure we perform ANA testing using IIFT on human tissue providing the most accurate and precise information to our patients on this critical autoimmune disease test. This test also includes Anti-mitochondrial antigen (AMA M2) associated with the autoimmune liver disease. Separately, we also perform LKM1 antibody test for liver disease.
Ref: Tozzoli et al (2002). Am J Clin Pathol. PMID: 11863229
Immunoblot scan for ANA Subsets Antibodies
In autoimmune diseases such as lupus autoantibodies are generated against several nuclear antigens including DNA, centromere, ribosomal and other proteins. The ANA subsets test is performed using the sensitive Immunoblot (IB) assay and tests for 17 antigens in a single blood sample, providing a comprehensive and rapid evaluation of ANA associated autoimmune diseases.
The following auto-antibodies are tested in this single test:
Mi-2, Ku, RNP/Sm, Sm, SS-A native (60 kDa), Ro-52 recombinant, SSB, Scl-70, PM-Scl100, Jo-1, Centromere B, PCNA, dsDNA, Nucleosomes (NUC), Histones, Ribosomal Protein, AMA-M2
Ref: Op De Beéck et al. (2012). Autoimmun Rev. PMID: 22387973.

Immunoblot scan for ANCA Antibodies
Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) are causative for ANCA vasculitis, a severe autoimmune inflammatory disease affecting the kidneys and lungs. Detection of ANCA antibodies is diagnostic for ANCA vasculitis though p-ANCA antibodies are present in other autoimmune diseases such as lupus as well. Anti-PR3 antibodies (cANCA) are present in 80% of patients suffering from Granulomatous polyangiitis (GPA). If detected early ANCA associated vasculitis has excellent treatment with chemical and biological agents.
This test is performed using the sensitive Immunoblot (IB) assay and not only detects anti-PR3 (cANCA) and anti-MPO (pANCA) but also anti-GBM antibodies in a single blood sample.
Ref: Csernok et al. (2018). J Immunol Methods. PMID: 29395165.
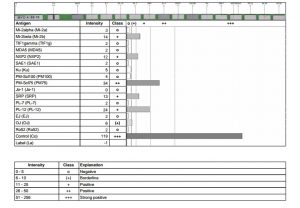
Immunoblot scan for myositis panel of a patient with inflammatory myositis (Photo copyright ImmunoCure Laboratory)
Differentiating inflammatory from degenerative myopathies is a challenge at the initial presentation. Moreover, the clinical spectrum of several inflammatory myopathies also overlaps making exact diagnosis difficult. The Myositis panel offers a range of antibodies to accurately diagnose inflammatory myositis which helps in prognosis and therapeutics. Antibodies directed against MDA5, Mi-2, SRP and tRNA synthetases (OJ, EJ, PL-12, PL-7, Jo-1), PMScl100, Ku antigens can be tested in a single blood test using the Immunoblot assay. MDA5 is a special syndrome resembling SLE and dermatomyositis (DRM) with rapidly progressive respiratory failure. TIF1 is associated with DRM with ~ 60% frequency of malignancy. Both MDA5 and TIF1, therefore, require urgent diagnosis which this panel provides.
Ref: Betteridge et al. (2011). Arthritis Res Ther. PMID: 21457520.